Project Number: 25-769.01.632-scl-akv-hazop
HAZOP Study Serial Number: 632
Project Overview
A Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study was conducted for the manufacturing of a proprietary chemical, Mesotrione, at Superform Chemistries Limited (SCL) earlier recognised as United Phosphorus Limited (UPL), Ankleshwar, Gujarat, in accordance with IEC 61882:2001 – Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP Studies) – Application Guide. The objective was to systematically identify potential hazards and operability issues arising from deviations from design and operating intent.
The study involved critical project documents like Piping and Instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Cause and Effect (C&E) diagrams etc. A multidisciplinary team reviewed causes, consequences, safeguards, and risk levels, and gave recommendations to enhance process safety, reliability, and emergency preparedness.
Objective
The objective of the HAZOP study was to systematically identify potential hazards and operability issues associated with the Mesotrione manufacturing plant and its associated systems, and to reduce the likelihood and consequences of incidents that could impact personnel safety, plant integrity, environmental performance, and operational reliability.
Methodology
HAZOP Preparation
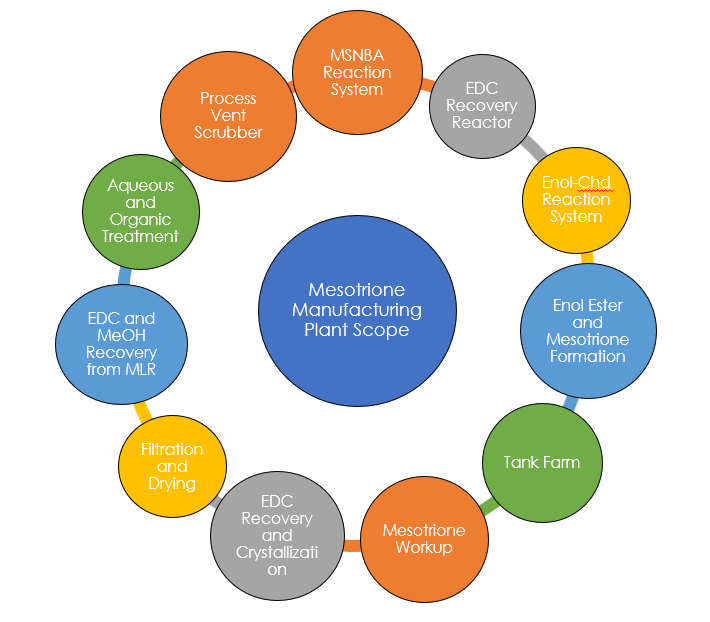
As the process of Mesotrione manufacturing is the trade secret of the Superform Chemistries Limited, hence critical document required for HAZOP preparations were not shared for back-office preparations. Therefore, in this particular project we adopted a different strategy. The preparation work such as Node Marking, Node-Description, Worksheet Pre-population was carried alongside the actual HAZOP Session at the Superform Chemistries Limited, Ankleshwar Facility. This is particularly challenging as simultaneously multiple activity was performed and required deep understanding and experience in the subject. The nodes identified were discussed and finalised with SCL team before the start of the HAZOP Study.
Opening Meeting
Opening Meeting
We initiated the on-site HAZOP process with an opening meeting. The agenda of the opening meeting was as:
- Introduction of HAZOP team members.
- Define the HAZOP methodology to HAZOP team.
- Clarify roles of the members in HAZOP Team.
- Process understanding by process/operations so that entire team gets familiar with the manufacturing process.
- Review of Material Safety Data Sheets so that team has prior information on all the hazards of the chemicals used/handled during the process.
- Review of thermal hazard / reaction calorimetry tests reports such as RC, DSC etc.
HAZOP Brainstorming Session
The HAZOP process was based on the principle that a team approach to hazard analysis will identify more problems than when individuals working separately combine results. The HAZOP team involved was combined of individuals with varying backgrounds and expertise. The expertise was brought together during HAZOP sessions and through a collective brainstorming effort that stimulates creativity and new ideas, and a thorough review of the process under consideration was made.
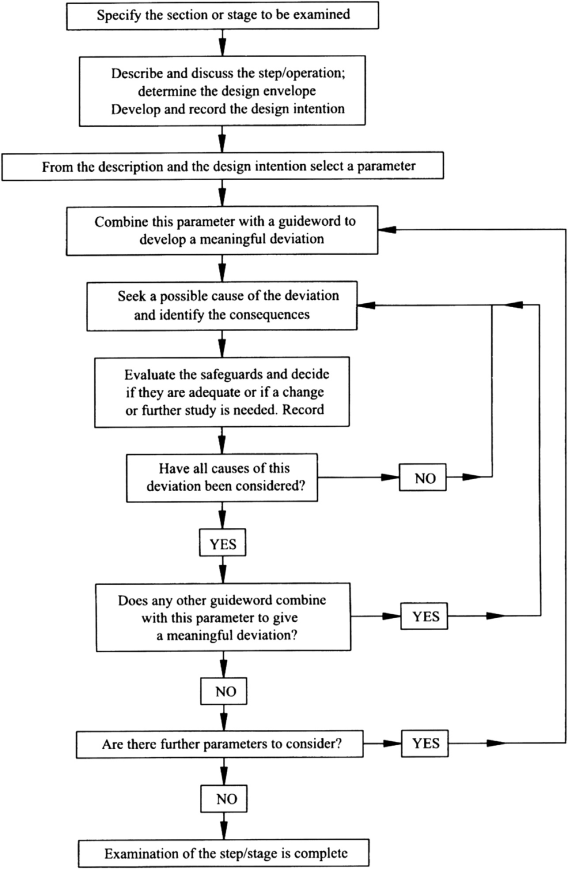
The HAZOP team focused on specific Nodes, which were identified before the start of the study. A process parameter was identified, say flow, and an intention is created for the node under consideration. Then a series of guidewords was combined with the parameter “flow” to create deviations. For example, the guideword “no” was combined with the parameter flow to give the deviation “no flow”. The team then focused on listing all the credible causes of a “No flow” deviation beginning with the cause that can result in the worst possible consequence the team can think of. Once the causes are recorded the team listed the consequences, safeguards and any recommendations deemed appropriate. The process was repeated for the next deviation and so on until completion of the node and was repeated for all the Nodes under consideration.
Key distinctive characteristics of HAZOP:
- HAZOP was carried using Sphera PHA Pro software and following format was used:
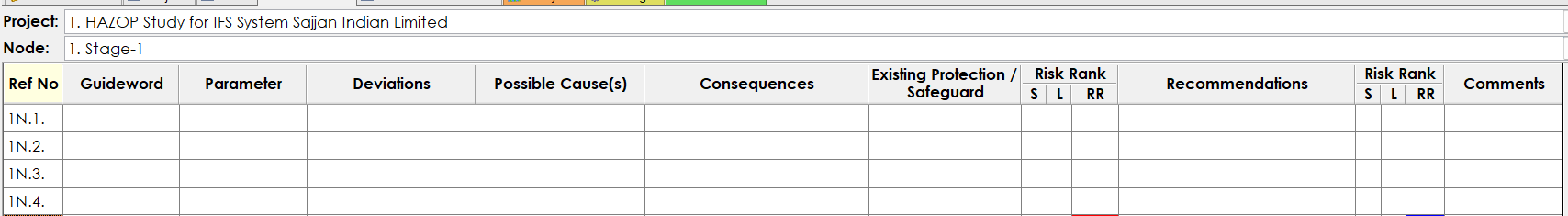
- Risk Ranking was carried out in 3 stages, that is initial potential risk after consequence, mitigated risk after existing safeguards and residual risk after HAZOP recommendations if any.
- Fundamentals of Independent Protection Layer (IPL) was used while identifying existing safeguards and also while providing any recommendation.
- Various national and internationally accepted guidelines, standards and documents were used in the Study such as:
- IEC 61882:2001
- Centre for Chemical Process Safety
- Gujarat Factory Rules
- Relevant Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
- Indian and International Standards
- ECHA for chemical information
- Rules followed for identifying safeguards:
- Rule 1: Safeguards should act before the event happens
- Rule 2: Approach for deciding type and number of Safeguards. For example: if 4 safeguards are required to meet the risk in ALARP (As Low as Reasonably Practicable) region, then minimum of 2 must be preventive, and 2 can be mitigative. Also, not more than 1 admin control should be there, SIS/SIFs and mechanical safeguards should also be there in adequate number.
- Rule 3: Safeguards should be Measurable and Auditable (demonstrate the performance)
- Rule 4: Safeguards should be independent.
- Rule 5: Safeguards have the different Probability of Failure on Demand (PFD) and Risk Reduction Factor (RRF).
- Rule 6: In HAZOP, consider failures of process control, not protection layers or safeguards.
- Rule 7: In Case of Redundancy of Safeguard, consider Single layer of Protection
- Rule 8: If Two Layer of Protection/Safeguards in Series, consider one. For example, RD and PSV in series are considered as one single safeguard.
- Rule 9: If Two Transmitters on same nozzle, consider Single protection layer
- Where existing safeguards were partial or incomplete, credit for risk reduction was not taken until the recommended actions were implemented. Such safeguards were marked as CNT (Credit Not Taken).Also, Risk Reduction Factor (RRF) for safeguards used was mentioned along with the safeguards.
- Detailed description of Nodes, Deviation, Cause, Consequences, Safeguards and Recommendations
- HAZOP team did a detailed analysis and all the recordings are made in such a descriptive manner that it is easy to understand.
Key Outcomes
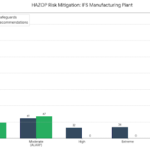
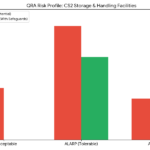
- Initial risk ranking without safeguards identified a significant number of High and Extreme risks. With the application of existing safeguards, many risks were reduced; however, some still required additional mitigation against which HAZOP team gave recommendations.
- Acceptable and Tolerable risks are largely well controlled by existing safeguards; HAZOP team gave recommendations in few actions for further improvement.
- All the cases of Intolerable and Unacceptable risks were mitigated by HAZOP recommendations with some cases recommended for further analysis/study.
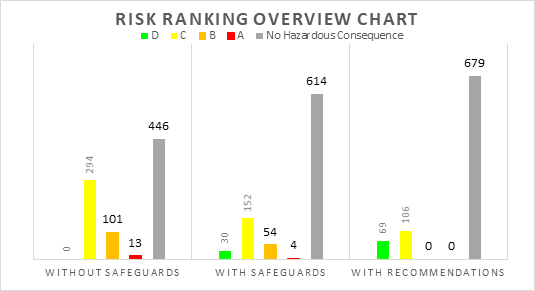
- The following table and graph highlights the risks of the consequences managed by the HAZOP team. Overall, 854 consequences were analysed by the HAZOP team.
| Risk Class | Without Safeguards | With Safeguards | With Recommendations |
| D (Acceptable) | 0 | 30 | 69 |
| C (Tolerable with ALARP) | 294 | 152 | 106 |
| B (Intolerable) | 101 | 54 | 0 |
| A (Unacceptable) | 13 | 4 | 0 |
| No Hazardous Consequence | 446 | 614 | 679 |
| Total | 854 | 854 | 854 |
Conclusion
The HAZOP study concluded that the Mesotrione manufacturing plant is fundamentally well-designed with robust safeguards. Implementation of the recommendations will further enhance process safety, operational reliability, and emergency preparedness. Overall, the case study demonstrates the importance of systematic hazard identification, multidisciplinary participation, and implementation of recommendations in achieving safe and reliable complex operations involved in the Mesotrione processing.