Project Number: 24-718.50.02-tuvrh-bct-hse
- Project Overview
A Hazardous Area Classification (HAC) Study was carried out to identify and classify areas where flammable gases, vapors may be present due to LNG the storage and handling at Liquified Natural Gas (LNG)/ Liquified Compressed Natural Gas (LCNG) stations of Dahej, Porbandar and Surendranagar, Gujarat. The study evaluates potential sources of and defines hazardous zones based on the likelihood and duration of the presence of explosive atmospheres.
The objective of the HAC Study was to establish appropriate hazardous area zoning and temperature classification to support the safe selection and installation of electrical and instrumentation equipment, thereby minimizing the risk of fire and explosion. The study was conducted in line with Indian Standard 5572. Considering the nature of chemicals handled, Adani Total Gas places strong emphasis on effective hazardous area classification to enhance personnel safety, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain safe and reliable plant operations without compromising operational efficiency.
The study involved analysis of critical project documents like Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs), Material Safety Data Sheets, Site Layout, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Inventory Data etc.
- Objective
The purpose of the Hazardous Area Classification study is to determine the extent of the hazardous areas around equipment handling or storing Natural Gas, both liquid and vapors in terms of Zone 0, Zone 1 and Zone 2.
The aim of hazardous area classification is to avoid ignition of those releases that may occur from time to time in the operation of facilities handling flammable liquids and vapors. The approach is to reduce to an acceptable minimum level the probability of coincidence of a flammable atmosphere and an electrical or other source of ignition occurring. In Hazardous Area Classification the extent of the hazardous areas around equipment handling or storing Natural gas, both liquid and vapors is determined in terms of Zone 0, Zone 1, and Zone 2.
- Methodology
- Data Collection and Review
Relevant process and safety information is collected and reviewed, including process flow diagrams (PFDs), Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs), Site layout drawings, material safety data sheets (MSDS), operating conditions (pressure, temperature), inventories of flammable materials, and details of existing ventilation systems.
- Identification of Flammable Materials
All flammable gases and vapours handled, processed, or stored within the facility are identified. Their physical and chemical properties such as flash point, boiling point, vapour density, lower and upper explosive limits, and auto-ignition temperature are reviewed to assess their hazardous characteristics.
- Identification of Sources of Release
Potential sources of release are identified for each area, including valves, flanges, pump seals, vents, drains, sampling points, and storage tank openings. Releases are categorized as Continuous grade, Primary grade and Secondary gradeas defined in IS 5572.<br>
- Assessment of Frequency and Duration of Release
Each identified source is evaluated to determine the likelihood and duration of release during normal operation, maintenance, or abnormal conditions. This assessment forms the basis for determining the extent and type of hazardous zone.
- Evaluation of Ventilation Conditions
The effectiveness of natural and/or mechanical ventilation is assessed, considering enclosure, air movement, and dispersion characteristics. Ventilation plays a key role in defining the extent of hazardous zones and their classification.
- Classification of Hazardous Zones
Based on the grade of release and ventilation conditions, areas are classified into:
- Zone 0 – explosive gas atmosphere present continuously or for long periods
- Zone 1 – explosive gas atmosphere likely to occur in normal operation
- Zone 2 – explosive gas atmosphere not likely to occur in normal operation and, if it occurs, will exist for a short period only
The horizontal and vertical extent of each zone is determined in accordance with IS 5572 guidance.
- Grouping and Temperature Classification
Flammable substances are assigned appropriate Gas Groups (IIA, IIB, IIC, IIIA, IIIB, IIIC) and Temperature Classes (T1 to T6) to ensure correct specification of electrical and instrumentation equipment suitable for use in the classified areas.
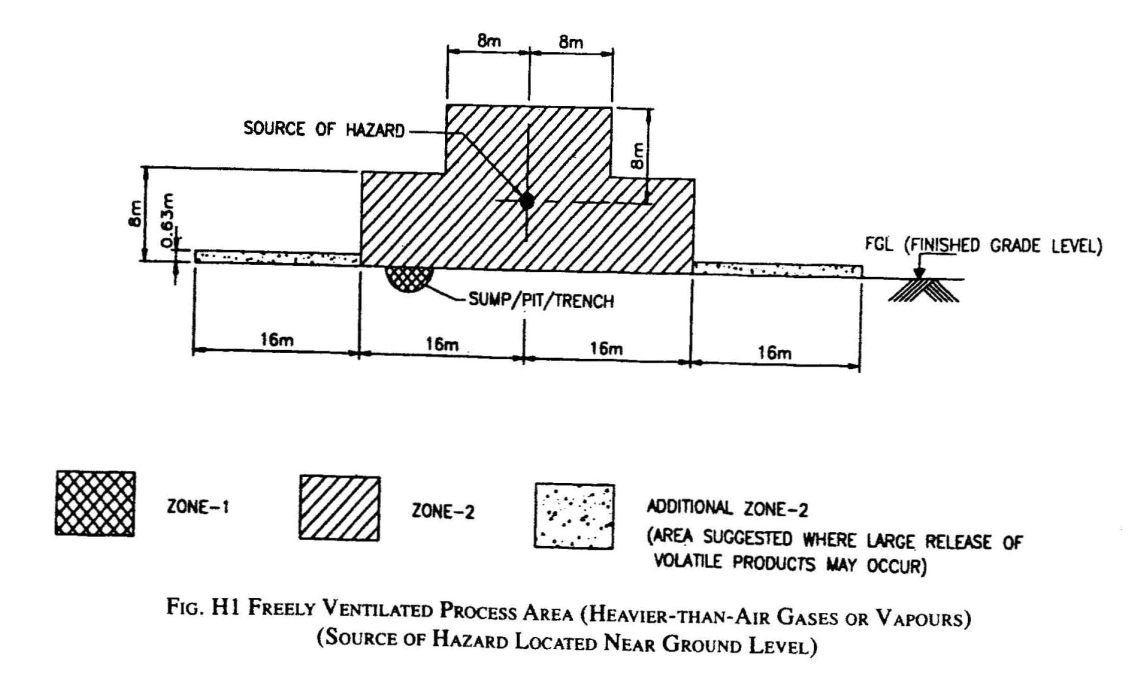
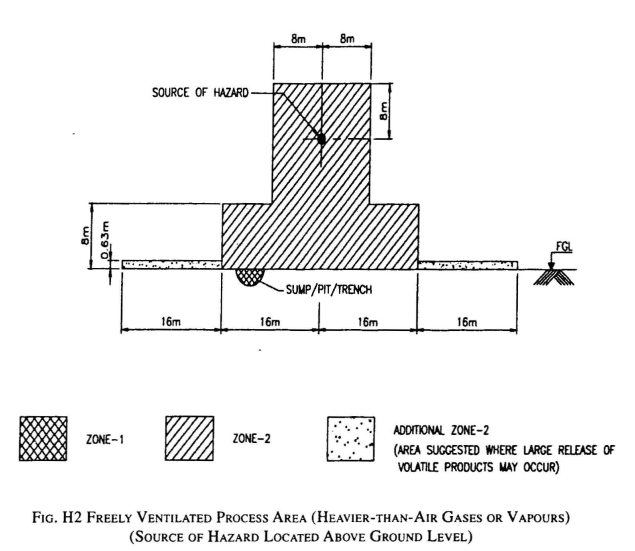
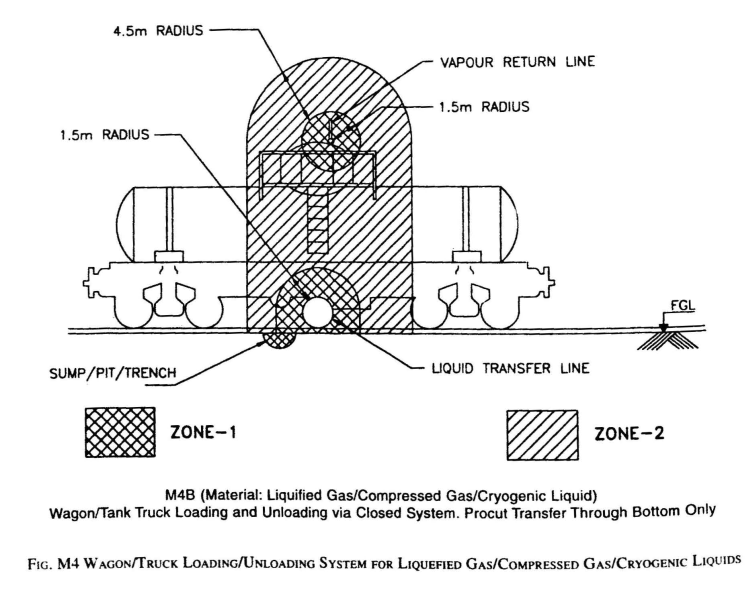
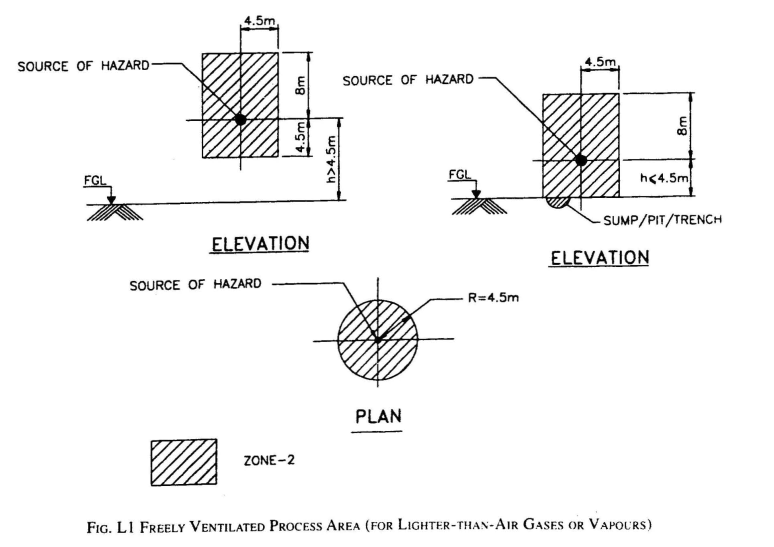
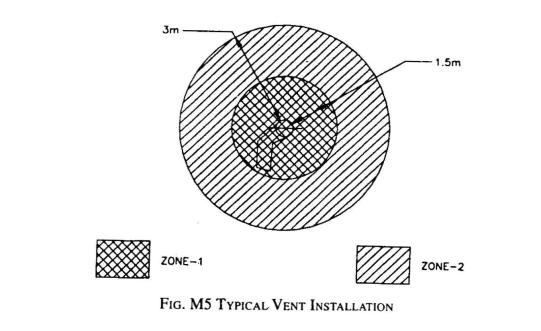
Key distinctive characteristics of HAC:
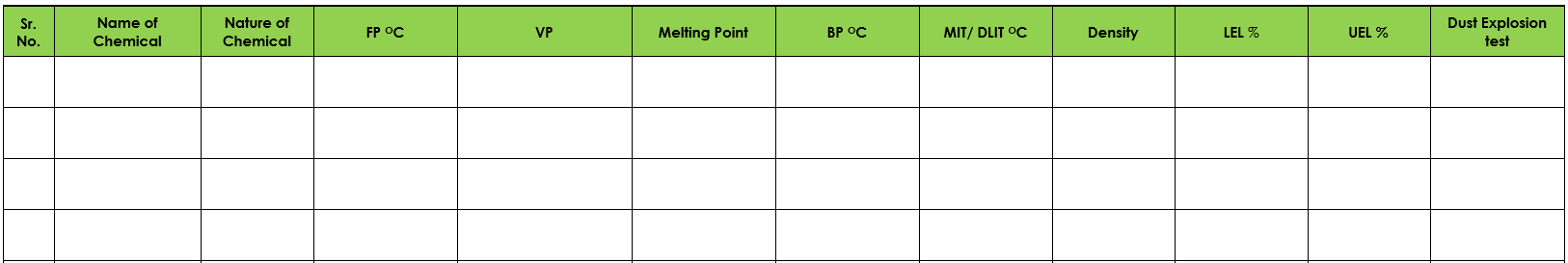
- A detailed list of Properties of chemicals such as LNG, and odorant used were provided for better analysis of material property and facilitate the HAC Study.
- Detailed HAC Schedule presented with all the required essential parameters on which Zoning is determined
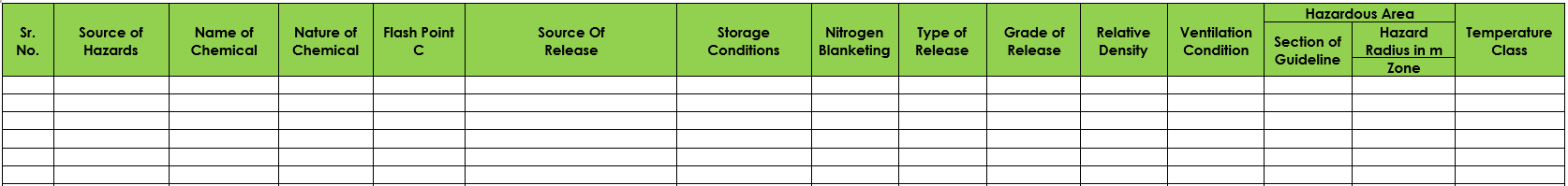
- Various Source of releases considered example: Leakage of bellow/ Nozzles/ Instrument Nozzles/ Flanged Joints/Tube, Vent of Vessel, Pump seals etc.
- All the assumptions made during the HAC Study were clearly marked, defined and documented.
- Key Outcomes
- Compatible electrical fittings to be ensured for Zone 0, 1, 2 for the area identified in Hazardous Area Classification.
- The temperature class of electrical equipment (Maximum allowable surface temperature) should be based on Auto-Ignition Temperature of explosive material.
- LNG was placed under temperature class T1 and any electrical apparatus suitable for T1 to T6 can be used as it has a very high Autoignition temperature and gas group of IIA.
- Mercaptan used as odorant has relatively lower auto-ignition temperature and hence placed under T3 temperature classification.
- As there are always risk of fire handling flammable Natural Gas, some recommendations were also provided in line with good practices followed in industry such as Implementing preventive maintenance schedules for critical equipment, static earthing, adhering to hot work guidelines and adequacy of lightning arrestor
- Conclusion
The Hazardous Area Classification (HAC) study concluded that areas handling or associated with flammable gases, vapors, liquids, at Adani Total Gas LNG/LCNG stations. The classification establishes extent of Zones and provides a sound basis for the selection and installation of suitable electrical and instrumentation equipment. Overall, the study demonstrates the importance of systematic hazardous area classification and adherence to applicable standards in ensuring safe, reliable, and regulatory-compliant operation of the LNG/LCNG facilities.




